Plasmons are collective excitations of free electrons in metals, such as Au, Ag or Cu, that, when stimulated by an energy source, such as sunlight, or a laser. A harmonic oscillation of the surface charges is induced with a wave-like behavior. In the process, they scatter light that can be read by a spectrometer, which captures and categorizes light according to its wavelength [1].
Silver deposition porocesses are very reproducible because the silver nanoparticle size distribution under identical deposition conditions is rather similar, to the benefit of potential industrial applications [2]. Ultrathin layers deposited on PMP could select and amplify specific wavelengths in order to enhance the electrical outcome of the photo-piezo-electric systems designed in the frame of PULSE-COM project.
Samples preparation
For the purpose of this study, different silver depositions have been made on three kind of substrates: thick PET (PET), thin PET (PETs) and on BK7 type optical glass (OG). The Ag film thickness had been varied from 1 to 9 nm with a 2 nm step.
Analytical techniques
The atomic force microscope (AFM) used is a XE100 model from Park System, model XE100. It has the capability to scan the samples in contact mode, non-contact mode and intermittent contact mode to provide information of local roughness. The maximum horizontal scan range is about 50×50 μm2 and the maximum vertical movement is 8 μm. A lateral resolution of tens of nano-meters can be achieved. The maximum image (data) resolution is 1024×1024 pixels. Images of samples of 1 and 5 nm thick Ag deposition on optical glass are presented below.
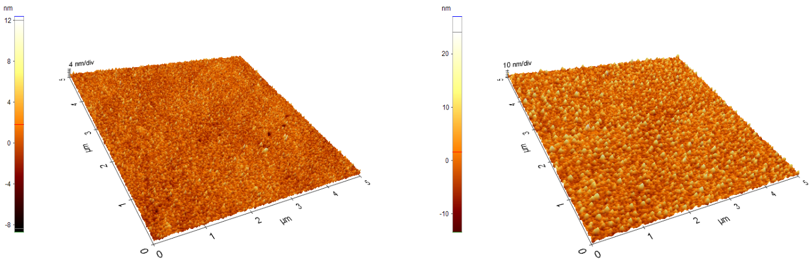
AFM images of samples of 1 (left) and 5 nm (rigth)thick Ag deposition on optical glass
A scanning electron microscope (FEI QUANTA INSPECT S) was used to observe the structures and morphology of the samples. A thin layer of gold was sputtered onto the samples prior to imaging. Images of samples of 1(left) and 5 nm (right) thickness on OG are presented below.

SEM images of samples of 1 (left) and 5 nm (right) thick Ag deposition on OG
The transmittance, reflectance and absorption were measured with an UV-Vis Lambda 35 (PerkinElmer) Spectrophotometer, Range: 190 – 1100 nm, Bandwidth: 0.5 – 4 nm (our samples were analysed with a 1 nm slit), Absorbance range (linearity 0.99 r2): 3.2 A, working temperature: 15°C, 35°C, Relative humidity: 20%, 80%, Precision: up to 0.1 nm, Scanning rate: 60 – 2,880 nm/min (our samples – 240 nm/min). Transmittance of the samples of 1, 5 and 9 nm thickness on PET (left) and OG (right) is presented below.
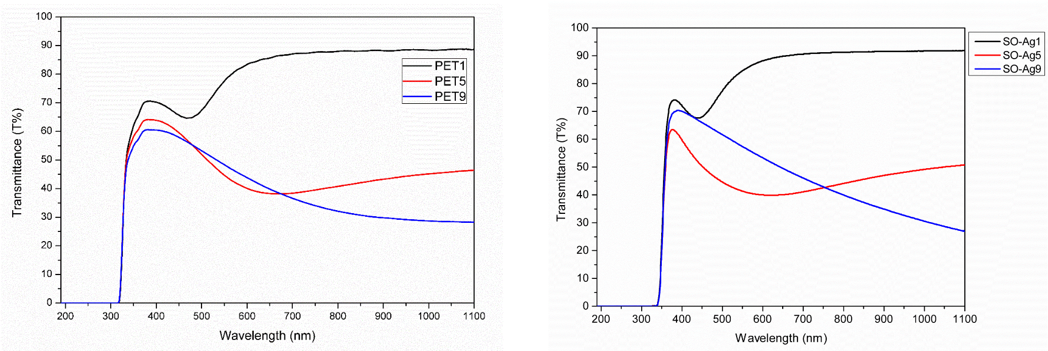
Transmittance of the samples of 1, 5 and 9 nm thick Ag deposition on PET (left) and OG (right)
The refraction index (n) and k factor, important for the optical behaviour of the designed systems were calculated using data collected with a Spectro-ellipsometer VVASE with a spectral range of 250-1700 nm at three angles of incidence: 60°, 65° and 70°. From measurement of amplitude ratio Ψ and the phase difference Δ at each wavelength and at different angle of incidents, optical models are generated by WVASE32 software and the n, k parameters and roughness are measured.
The refraction index of the samples of 7 and 9 nm thickness on PET (left) and OG (right) is presented below
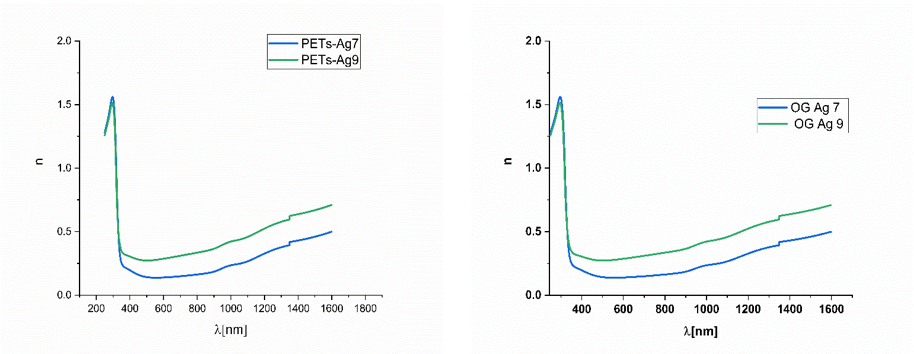
The refraction index of the samples of 7 and 9 nm thick Ag deposition on PET (left) and OG (right)
Conclusions
Ultrathin Ag films of 1, 3, 5, 7 and 9 nm thickness were deposited by RF Magnetron Sputtering onto glass and PET substrates.
Samples were morphologically analysed by AFM showing roughness of up to 3 nm.
The films’ refractive index was obtained by means of spectroscopic ellipsometry data using Drude and General Oscillator models-based technique by minimizing the difference between the measured spectrum of the ellipsometric parameters and the values calculated from the model.
The calculated refractive index n present 0.1-0.6 values in the 345-1200 nm region.
The transmittance and reflection of the samples, investigated using UV-Vis-NIR spectroscopy, show a transmission maximum specific to Ag and a transmittance minimum at about 500 nm, which depends on the thickness of the deposited film, showing the appearance of surface plasmon resonance at low thickness of films, meaning 1, 3 and 5 nm.
The film of 3 nm thick was chosen to be deposited on PMP to increase the electrical response and to induce a wavelength selection to designed materials.
[1]Hoggard A, Wang LY, Ma L, Fang Y, You G, et al. Using the Plasmon Linewidth to Calculate the Time and Efficiency of Electron Transfer between Gold Nanorods and Graphene. ACS Nano 7(12) (2013) 11209-11217
[2]Sarita Marom, Monique Dorresteijn, Ritika Modi, Alessandro Podestà, Marcel Di Vece. Silver nanoparticles from a gas aggregation nanoparticle source for plasmonic efficiency enhancement in a-Si solar cells. Materials Research Express, 6 (2018) 045012


